Tuesday, 17 May 2022
By Linda Tomy
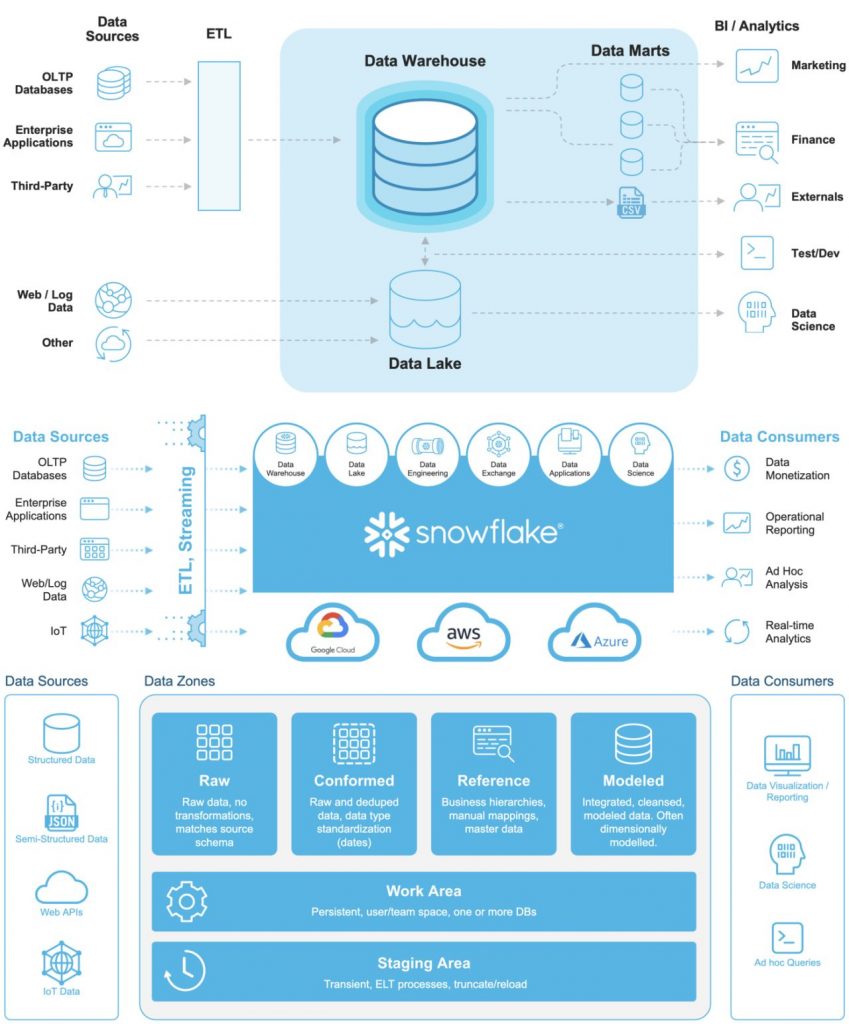
Modern Data Infrastructure
We have given solutions to our client’s modern era data problems. Most of the enterprises have a staggered data approach wherein they are having a separate data architecture for each of their digital product. We always propose to have a defined data infrastructure which fits the purpose of enterprise-wide data strategy. Data infrastructure contains wide ranges of technologies, tools and systems to deal with dozens of steps and features that can be applied on a data point. This helps understand the complexities and details pertaining to different data objects. Data infrastructure contains wide ranges of technologies, tools and systems to deal with dozens of steps and features that can be applied on a data point.
FEATURES:
1. Data Source
2. Data Destination
3. Data Ingestion
4. Data Migration
5. Data Replication
6. Wrangling & Data Cleaning
7. Parsing & Business Logic
8. Data Analytics
9. Data Consumption
10. Data Transfer
11. Data Intelligence
COMPONENTS:
1. Data Storage
2. Data Warehouses
3. Data Pipelines
4. DataOps
5. Data Lakes
6. Data Analytics Tools
7. Data Observability Tools
MANAGEMENT:
1. Organization
2. Metadata
3. Reference Data
4. Governance
5. Policies
6. Standards
7. Rules
DATA ITSELF IS IN DIFFERENT FORMS:
1. Raw (Non qualitative)
2. Semi Structured
3. Unstructured
4. Structured
5. Domains
6. Entities
7. Files
8. Documents
DATA GENERATION:
1. Applications
2. Systems (Services)
3. Softwares
4. IoT Devices
5. Business Transactions
6. Batch Processes
7. Internal Processes
8. Log Platforms
9. Monitoring Tools
10. Observability Tools
11. Digital Platforms
12. Other Products
13. Mobile or Web Apps
DATA PIPELINES:
Similar concept in data infrastructure is data pipeline which covers all the phases of data from its source (either through batch, real time, events, logs or database triggers) till its destination (file, document, non relational or relational database, data warehouse, BI tools, analysis tools, observability platform or a different replication, migration service).
Between source and destination data can be modified, parsed, transferred, analyzed, ingested, replicated, transferred to other systems, platforms, databases and applications. All those different phases between data source (where it gets created) and data destination (where it resides) are considered part of enterprise data pipeline.
Any organization or an enterprise will have its own business requirements, strategies and needs resulting in their own flavor of software products, digital services and their own data pipeline using tools, technologies, standards, governance, policies and organization as per their limitations, constraints and needs.
There are different design patterns for data pipelines for fault tolerance, data reliability and accuracy, real time, batch, cloud, event driven, distributed or big data systems and platforms. Similarly, different big data tools can provide more features for searching, storing, replicating and parsing huge and different types of data. ETL (Extract, Transform and Load) is limited as compared to data pipeline which can apply rich business logic and application features on different sets of data be it structured or un structured.