Kubernetes In-Place Pod Resize
Posted on Jan 16, 2026What is In-Place Pod Resize?
Previously, the CPU and memory resources allocated to a container within a Pod were immutable. Consequently, modifying these resources necessitated the deletion and recreation of the entire Pod. This operation proved highly disruptive for stateful services, batch jobs, and latency-sensitive workloads.
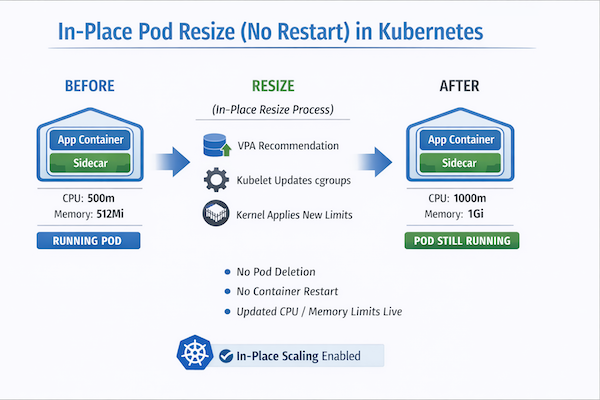
Starting Kubernetes 1.35, the In-Place Pod Resize moves to stable version, which enables the adjustment of CPU and memory requests and limits within a running Pod, often without requiring a container restart.
Key Concept:
Desired Resources: The container’s spec.containers[*].resources field now represents the desired resources. For CPU and memory, these fields are now mutable.
Actual Resources: The status.containerStatuses[].resources field reflects the resources currently configured for a running container.
Triggering a Resize: A resize can be requested by updating the desired requests and limits in the Pod’s specification using the new resize subresource.
Benefits of In-Place Pod Resize:
In-place Pod Resize serves as a foundational building block that facilitates seamless vertical autoscaling and enhances workload efficiency.
Resources Adjusted Without Disruption: Workloads sensitive to latency or restarts can have their resources modified in-place without downtime or loss of state.
Enhanced Autoscaling: Autoscalers are now empowered to adjust resources with reduced impact. For instance, Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA)’s InPlaceOrRecreate update mode, which utilizes this feature, has transitioned to beta. This enables automatic and seamless resource adjustments based on usage with minimal disruption.
Address Transient Resource Needs: Workloads that temporarily require additional resources can be adjusted promptly. This enables features such as the CPU Startup Boost, where applications can request more CPU during startup and then automatically scale back down.
Examples of Use Cases:
- A game server that requires adjustments in size based on fluctuating player counts.
- A pre-warmed worker that can be shrunk while unused but inflated upon the first request.
- Dynamically scale with load for efficient bin-packing.
- Increased resources for JIT compilation on startup.
Changes between beta (1.33) and stable (1.35):
Since the initial beta in v1.33, development effort has primarily been focused on stabilizing the feature and enhancing its usability based on community feedback. Here are the primary changes for the stable release:
Memory limit decrease: Previously, decreasing memory limits was prohibited. This restriction has been lifted, and memory limit decreases are now permitted. The Kubelet attempts to prevent OOM-kills by allowing the resize only if the current memory usage is below the new desired limit. However, this check is best-effort and not guaranteed.
Prioritized resizes: If a node lacks sufficient space to accommodate all resize requests, Deferred resizes are reattempted based on the following priority:
PriorityClass
QoS class
Duration Deferred, with older requests prioritized first.
Pod Level Resources (Alpha): Support for in-place Pod Resize with Pod Level Resources has been introduced behind its own feature gate, which is alpha in v1.35.
Increased observability: There are now new Kubelet metrics and Pod events specifically associated with In-Place Pod Resize to assist users in tracking and debugging resource changes.
Improved stability:
Resolve kubelet-scheduler race conditions: There are known race conditions between the kubelet and scheduler with respect to in-place pod resize. Work is underway to resolve these issues over the next few releases.
Safer memory limit decrease: The Kubelet’s best-effort check for OOM-kill prevention can be made even safer by relocating the memory usage check into the container runtime itself.
Posted in DevOps, Kubernetes
Tagged in containerresourceupdate, in-place-resize, kubernetes

