Building a Scalable Data Platform Using Open Source Technologies
Data Platform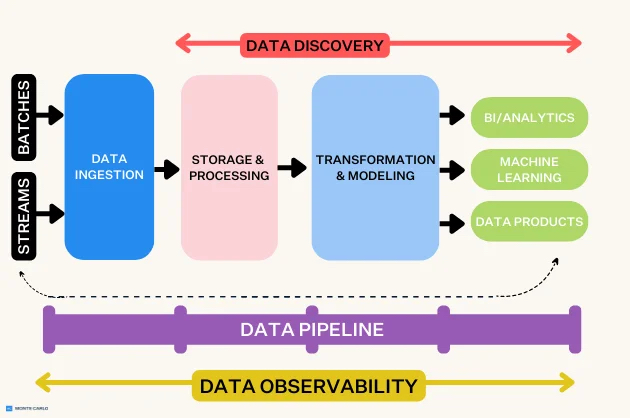
Introduction
As organizations increasingly rely on data to drive decision-making, the need for scalable, cost-effective, and flexible data platforms has become paramount. This case study examines how a mid-sized enterprise successfully built a robust data platform using open-source technologies, enabling them to manage large volumes of data, improve data analytics capabilities, and reduce costs.
The Challenge
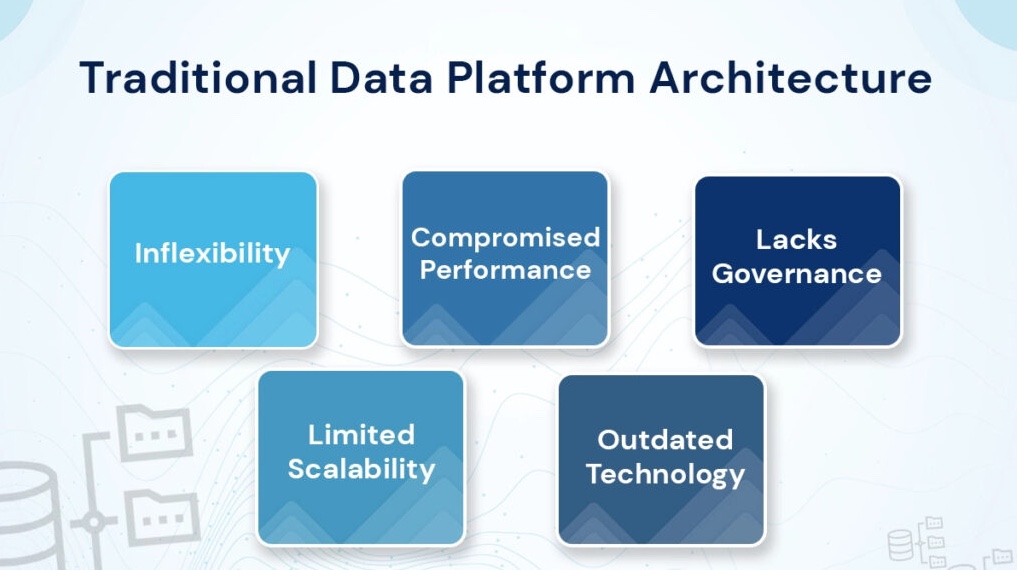
The organization faced several challenges related to its existing data infrastructure:
- Data Silos: Different departments were using separate data systems, leading to fragmented data storage and making it difficult to gain a unified view of the organization’s data.
- High Licensing Costs: The existing proprietary data solutions incurred significant licensing fees, which were becoming unsustainable as the organization’s data needs grew.
- Scalability Issues: The current infrastructure struggled to handle the increasing volume, velocity, and variety of data, leading to performance bottlenecks and slower analytics processing.
- Limited Data Access: Access to data was restricted to certain departments due to the complexity of the existing systems, limiting the ability to make data-driven decisions across the organization.
The Solution
To overcome these challenges, the organization decided to build a new data platform based on open-source technologies. The key components of the solution included:
- Apache Hadoop and Spark for Data Processing: The organization adopted Apache Hadoop for distributed storage and processing of large datasets, and Apache Spark for real-time data processing and analytics. This combination provided the scalability and flexibility needed to handle large volumes of data efficiently.
- Kafka for Data Ingestion: Apache Kafka was implemented as a distributed streaming platform to handle real-time data ingestion from various sources. Kafka’s ability to process high-throughput data streams made it ideal for the organization’s needs.
- PostgreSQL for Data Storage: For structured data, the organization chose PostgreSQL, an open-source relational database system. PostgreSQL’s robustness, scalability, and support for complex queries made it a suitable choice for their data storage needs.
- Airflow for Workflow Orchestration: Apache Airflow was used to manage and automate data workflows. This allowed the organization to schedule, monitor, and maintain complex data pipelines with ease.
- Grafana and Prometheus for Monitoring: To ensure the reliability and performance of the data platform, Grafana and Prometheus were integrated for real-time monitoring and alerting, providing insights into system health and performance.
- Open-Source BI Tools: The organization implemented open-source business intelligence (BI) tools, such as Metabase, to enable data visualization and reporting across departments. This democratized access to data, empowering employees to make data-driven decisions.
Implementation
The implementation of the open-source data platform was carried out in several steps:
- Planning and Architecture Design: The IT team, in collaboration with key stakeholders, designed a scalable architecture that could accommodate future growth and changing data needs. This involved selecting the appropriate open-source tools and defining data workflows.
- Pilot Project: A pilot project was launched to test the new data platform with a subset of the organization’s data. This phase helped identify any issues and refine the system before full-scale deployment.
- Data Migration: Data from the existing proprietary systems was carefully migrated to the new open-source platform, with minimal disruption to ongoing operations. This included setting up ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes to ensure data integrity and consistency.
- Training and Change Management: Training programs were provided to IT staff and end-users to ensure they were comfortable using the new tools and systems. Change management initiatives were also implemented to support the transition.
- Full Deployment and Optimization: After successful testing and training, the data platform was fully deployed across the organization. Continuous monitoring and optimization were carried out to ensure peak performance.
Results
The transition to an open-source data platform resulted in significant benefits:
- Cost Savings: The organization saved approximately 40% on licensing fees by moving away from proprietary solutions, freeing up budget for other strategic initiatives.
- Scalability and Performance: The new platform easily handled the organization’s growing data needs, processing large volumes of data more quickly and efficiently than the previous system.
- Unified Data Access: Data silos were eliminated, providing a unified view of data across the organization. This improved collaboration between departments and enabled more comprehensive data analysis.
- Improved Decision-Making: With easier access to data and powerful analytics tools, decision-making across the organization became more data-driven, leading to better business outcomes.
- Flexibility and Innovation: The use of open-source technologies provided the flexibility to customize and extend the platform as needed, enabling the organization to quickly adopt new technologies and innovations.
Conclusion
This case study demonstrates the power and potential of open-source technologies in building a scalable, cost-effective data platform. By leveraging tools like Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, and PostgreSQL, the organization was able to overcome the limitations of its legacy systems, enhance its data capabilities, and achieve significant cost savings.
Future Outlook
The organization plans to continue expanding its data platform by incorporating advanced analytics capabilities, such as machine learning and predictive analytics. The open-source foundation of the platform provides the flexibility to easily integrate these new technologies, ensuring that the organization remains at the forefront of data-driven innovation.

